The article explores the potential for using the Model Context Protocol (MCP) as a primary backend interface instead of traditional REST APIs in AI-enabled applications. Through the Galaxium Travels experiment, it examines the advantages and disadvantages of an MCP-first architecture, advocating for its use to reduce duplication and complexity while acknowledging REST's established role in many ecosystems.
Testing AI Agents with the watsonx Orchestrate Agent Developer Kit (ADK)- Evaluation Framework – A Hands-on Example
The post outlines using the Evaluation Framework in watsonx Orchestrate ADK to verify AI Agent behavior through a practical example: Galaxium Travels, a fictional booking system. It details setting up the environment, defining user Stories, generating synthetic Test Cases, and running evaluations, crucial for ensuring AI reliability and transparency.
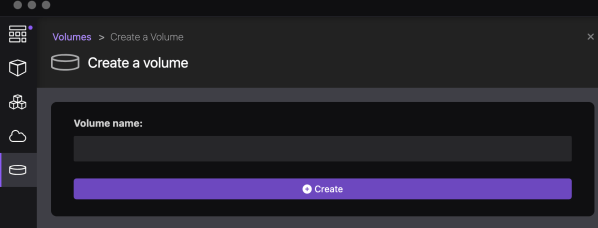
How do you handle access to the local filesystem data with Podman Desktop on macOS?
This blog post explores managing local filesystem access with Podman Desktop on macOS. It discusses two options: mapping an existing local folder as a volume to the container, and creating a local Podman volume and accessing data inside the container. Detailed steps for both approaches are provided, addressing potential access rights issues.
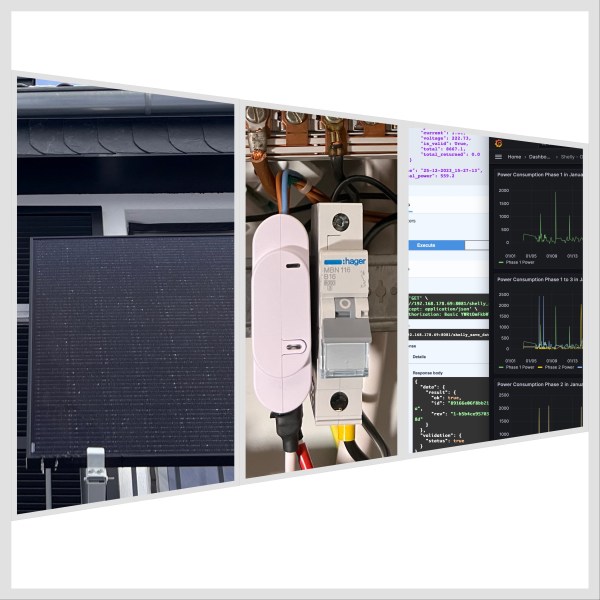
Unleash your creativity and design a custom visualization for the Shelly 3EM device with Grafana
The blog post details an example implementation of a connection server using Shelly 3EM, IBM Cloud Cloudant, and Grafana. It aims to store historical data for visualizing electricity consumption. The project involves detailed architecture, environment setup, Python, FastAPI, Podman, and more usage. The setup covers Raspberry Pi, Podman Compose, and IBM Cloud Code Engine environments, with prerequisites and detailed configurations. The approach allows users to monitor and visualize power consumption efficiently and cost-effectively using Grafana.
Build and push a container image to IBM Cloud Container Registry using bash automation
This extract is from a bash automation script in the question-answering GitHub project. The bash script automates the deployment to IBM Cloud Code Engine. The extraction is about the building and pushing a container to the IBM Cloud Container Registry.
Custom domain and TLS certificate for your application on IBM Cloud Code Engine
This blog post is about using the domain mapping functionality in IBM Cloud Code Engine to use custom domains and TLS certificates for your applications. The source code related to an example setup is in the GitHub project example WebApp build on Vue.js. But now we are going to use a wild card certificate for our domain *.example.com. With a TLS certificate for that domain.
Run Watson NLP for Embed on IBM Cloud Code Engine
This blog post is about using the IBM Watson Natural Language Processing Library for Embed on IBM Cloud Code Engine and is related to my blog post Run Watson NLP for Embed on your local computer with Docker. IBM Cloud Code Engine is a fully managed, serverless platform where you can run container images or batch jobs.
Open the door wide open for Watson Assistant with “custom extensions” – an awesome progression
IBM Watson Assistant is a SaaS offering from IBM to build conversational assistants. IBM Watson Assistant is using artificial intelligence which helps to understand users in context, to provide them easy and fast, consistent, and accurate answers across various applications, devices, or channels. IBM Watson Assistant is built on natural language understanding (NLU), natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML). The first version was already very good, and IBM clients and partners were starting to take these advantages; for example Watson Assistant was used at the International Space Station. Here you can find some more details: CIMON brings AI to the International Space Station. Based on the feedback from clients, the IBM development and design team has created a brand new experience and added new functionalities to the service for example they expanded the integration possibilities with extensions. In this blog post I focus especially on custom extensions development and setup.
Open the door for root users in Red Hat OpenShift (example StatefulSet)
This "blog post"/"cheat sheet" is about "Open the door for root users in OpenShift (example StatefulSet)". The topic is in context of two blog posts I wrote called Run a PostgreSQL container as a non-root user in OpenShift and Open the door for root users in Red Hat OpenShift¶.
Open the door for root users in Red Hat OpenShift (example Deployment)¶
This "blog post"/"cheat sheet" is about "Open the door for root users in OpenShift". The topic is in context of an older blog post I wrote called Run a PostgreSQL container as a non-root user in OpenShift. Let's look for the opposite perspective this blog post.