When working locally with IBM watsonx Orchestrate using the Agent Development Kit, I often want to test agents against local models instead of hosted ones.
For quick experiments, Ollama is usually the fastest path for this.
The pattern looks familiar and easy to automate:
- start Ollama
- verify the model endpoint
- reset the local Orchestrate setup
- register the model
- start chatting
Instead of repeating this manually, I use a small Bash script as a cheat sheet for a simple executable workflow.
The GIF below shows the interaction:
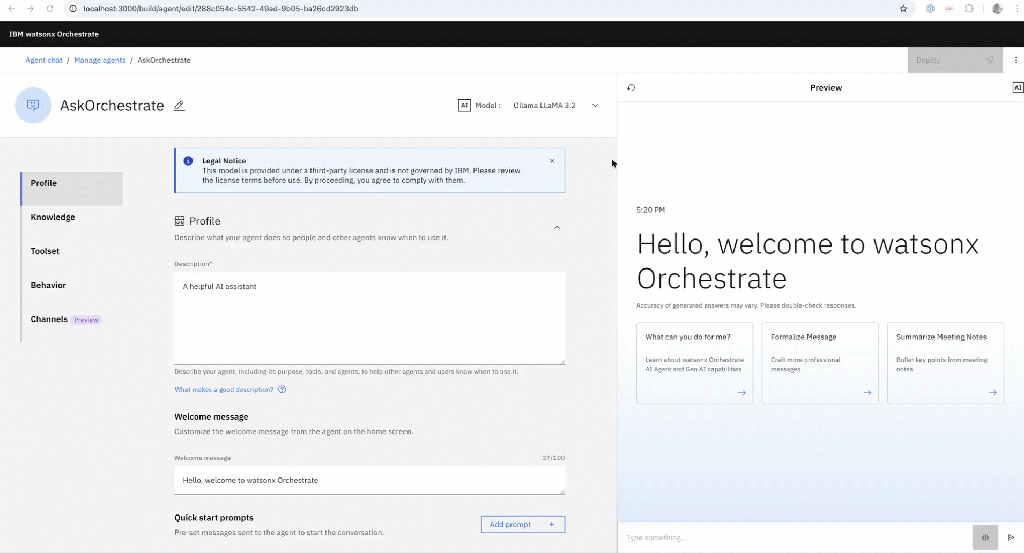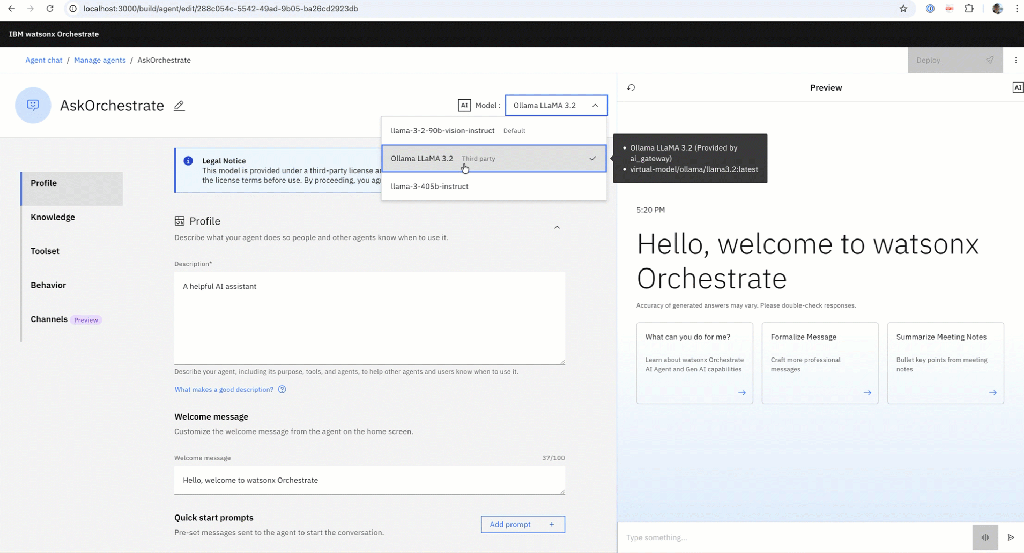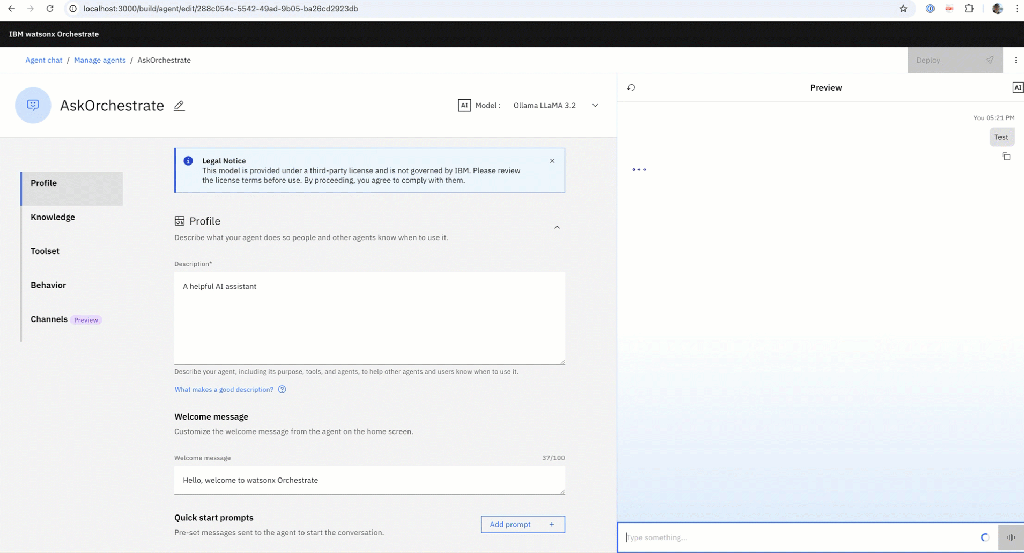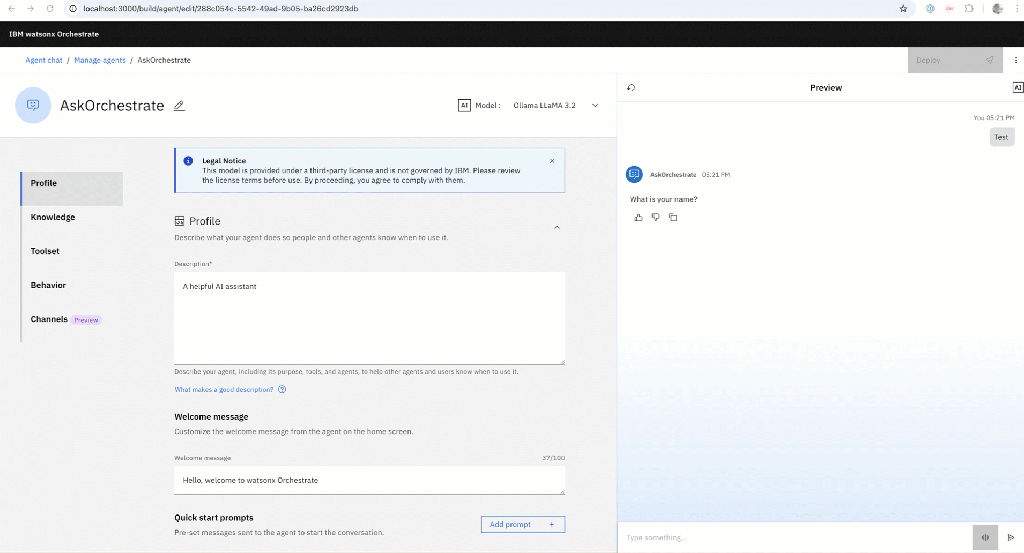
1. Why This Script Exists
Some of the setup can fail for very unexciting reasons:
- Ollama not listening on the expected interface
- wrong IP or port when running inside local orchestration
- environment variables not exported
- model registered, but not actually reachable
This script forces a known-good path:
First make Ollama reachable, then wire it into Orchestrate.
Nothing fancy — just disciplined automation.
2. What the Script Does (High-Level)
In one linear flow, using the two scripts:
First script:
- Starts Ollama on an explicit host and port
Second script:
- Lists and sanity-checks available Ollama models
- Verifies the Ollama
/v1/chat/completionsendpoint - Resets and starts the local Orchestrate server
- Activates the local Orchestrate environment
- Adds an Ollama-backed model (no connection required)
- Starts an interactive chat
- Streams relevant server logs
Colorized output is intentional — when something breaks, you want to see where immediately.
3. The Bash Cheat Sheets
- Start Ollama (first terminal)
# Colors for outputRED='\033[0;31m'GREEN='\033[0;32m'YELLOW='\033[1;33m'BLUE='\033[0;34m'NC='\033[0m'echo -e "\n${BLUE}========================================${NC}"echo -e "${YELLOW} Set Ollama port ${NC}"systemctl stop ollamaexport OLLAMA_HOST=0.0.0.0:11434ollama serve- Register Ollama in watsonx Orchestrate (second terminal)
# Colors for outputRED='\033[0;31m'GREEN='\033[0;32m'YELLOW='\033[1;33m'BLUE='\033[0;34m'NC='\033[0m'export ENVIRONMENT="draft"echo -e "\n${BLUE}========================================${NC}"echo -e "${YELLOW} List Ollama models ${NC}"ollama listecho -e "\n${BLUE}========================================${NC}"echo -e "${YELLOW} Test Ollama connection ${NC}"curl -X POST ${OLLAMA_CUSTOM_HOST}/v1/chat/completions \ -H 'content-type: application/json' \ -d '{ "model": "llama3.2", "messages": [{"content": "Hi","role": "user"}]}'read -p "Press enter to continue"echo -e "\n${BLUE}========================================${NC}"echo -e "${YELLOW} Activating virtual environment... ${NC}"source venv/bin/activateorchestrate server resetsource .envorchestrate server start \ --env-file .env \ --with-connections-ui \ --with-doc-processing \ --accept-terms-and-conditionsorchestrate env activate localorchestrate models listcd adk-project/model-gateway/export AGENTMODEL=${OLLAMA_AGENT_MODEL}echo "Model: ${AGENTMODEL}"echo -e "\n${RED}========================================${NC}"echo -e "${RED} Ollama does not require a connection ${NC}"PROVIDER_CONFIG="{\"api_key\":\"${OLLAMA_KEY}\",\"custom_host\":\"${OLLAMA_CUSTOM_HOST}\"}"orchestrate models add --name ${AGENTMODEL} --provider-config ${PROVIDER_CONFIG}orchestrate chat startorchestrate server logs | grep "ai-gateway-1"- Optional Model configuration file
name: ollama/OLLAMA_MODEL_TO_REPLACEdisplay_name: Ollama LLaMA 3.2description: | Ollama-hosted LLaMA 3.2 model for local or edge deployments.tags:- ollama- llamamodel_type: chatprovider_config: api_key: ollama custom_host: OLLAMA_URL_TO_REPLACEThe command to use the model configuration file.
orchestrate models import -f ./adk-project/model-gateway/model_gateway_config_ollama.yaml- Environment file template
The ipconfig getifaddr en0 command is important in this context to get the local network address. I do this during setting the environment variable: export OLLAMA_CUSTOM_HOST=http://$(ipconfig getifaddr en0):11434
# watsonx Orchestrateexport WO_DEVELOPER_EDITION_SOURCE=myibmexport WO_ENTITLEMENT_KEY=export WATSONX_APIKEY=export WATSONX_SPACE_ID=<ID>export WXO_API_KEY=${WATSONX_APIKEY}export WATSONX_REGION=us-southexport WATSONX_URL=https://${WATSONX_REGION}.ml.cloud.ibm.comexport ASSISTANT_LLM_API_BASE=${WATSONX_URL}export ASSISTANT_EMBEDDINGS_API_BASE=${WATSONX_URL}export ROUTING_LLM_API_BASE=${WATSONX_URL}export ORCHESTRATE_API_TOKEN=blablub# Ollamaexport OLLAMA_AGENT_MODEL=llama3.2:latestexport OLLAMA_KEY=ollamaexport OLLAMA_CUSTOM_HOST=http://$(ipconfig getifaddr en0):114344. Additional Resources
- IBM watsonx Orchestrate – Official Docs
https://developer.watson-orchestrate.ibm.com/ - watsonx Orchestrate CLI Reference
https://developer.watson-orchestrate.ibm.com/cli/ - Ollama Documentation
https://ollama.com/ - Ollama OpenAI-Compatible API
https://ollama.com/blog/openai-compatibility
I hope this was useful to you and let’s see what’s next?
Greetings,
Thomas
#watsonxOrchestrate, #Ollama, #LocalLLM, #AgenticAI, #AIAgents, #AIOrchestration, #LLMOps, #BashAutomation, #LocalAI

Leave a comment