This blog post contains information about a simple example implementation for a simple question-answering pipeline using an inside-search (IBM Cloud Watson Discovery) and a prompt (IBM watsonx.ai with prompt-lab) to create an answer.
The source code is in following GitHub project:
https://github.com/thomassuedbroecker/simple-qa-pipeline
This blog post is structured in:
- Objective
- Simplified Architecture
- Run the
simple-qa-pipelinelocally - Useful tools
- Summary
1. Objective
The objective is to implement an elementary question-answering pipeline example by showing how to consume existing REST APIs and create a REST API with fastAPI and Python because Python is well-known in the AI world.
Note: An excellent and detailed example implementation for a
question-answering pipelineis in thequestion-answering project. That project contains many more details and integrations; thequestion-answering pipelineis implemented in Java. The project also provides an example implementation for an experiment execution for the question-answering pipeline the service for the execution is calledexperiment-runnerand is implemented in Python. Niklas Heidloff has written many awesome blog posts about AI and thisquestion-answering project. I recommend briefly looking at the related blog posts to this project.
2. Simplified Architecture
The simple-qa-pipeline creates an answer to a question by using a Large Language Model inside watsonx with the Prompt lab and it searches for documents with Watson Discovery to provide the context.

3. Run the simple-qa-pipeline locally
In addition to this blog post, I created a YouTube Livestream about the blog post running the example on various runtimes :
- 01:21 The example
- 06:56 watsonx Prompt Lab
- 10:31 Running the example locally
- 17:37 Using Swagger UI (OpenAPI) for the example application
- 27:37 Running the example as a container
- 22:16 Building the prompt using the environment variables
- 27:25 Running the example on IBM Cloud Code Engine
3.1. Get the source code and create a virtual Python environment
- Clone project
git clone https://github.com/thomassuedbroecker/simple-qa-pipeline.git
- Create a virtual Python environment
cd simple-qa-pipeline/code python3.11 -m venv simple-pipeline-env-3.11 source ./simple-pipeline-env-3.11/bin/activate
- Install needed Python libs and create a
requirements.txtfile
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
python3 -m pip install "fastapi[all]"
python3 -m pip install requests
python3 -m pip install pydantic
python3 -m pip freeze > requirements.txt
#python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
3.2. Configure the simple-qa-pipeline to access the needed REST API by using environment variables
- Create
.envfile
cat ./.env-template > ./.env
- Outline of the environment file
# Discovery
export DISCOVERY_API_KEY=
export DISCOVERY_URL=https://api.us-east.discovery.watson.cloud.ibm.com/instances/ export DISCOVERY_COLLECTION_ID=
export DISCOVERY_PROJECT=
export DISCOVERY_INSTANCE=
# watsonx
export WATSONX_URL="https://us-south.ml.cloud.ibm.com/ml/v1-beta/generation/text"
export WATSONX_LLM_NAME=google/flan-ul2
export WATSONX_MIN_NEW_TOKENS=1
export WATSONX_MAX_NEW_TOKENS=300 export WATSONX_PROMPT="Document:\n\n<<CONTEXT>>\n\nQuestion:\n\n<<QUESTION>>\n\nAnswer:\n\n"
export WATSONX_PROJECT_ID= export WATSONX_VERSION="2023-05-29" # IBM Cloud export IBMCLOUD_APIKEY=
# APP
export APP_USER=admin
export APP_APIKEY=admin
3.3 Run simple-qa-pipeline server
source .env python3 simple-qa-pipeline.py
- Open Swagger UI with the API documentation
open http://localhost:8081/docs

3.4. Run a small test
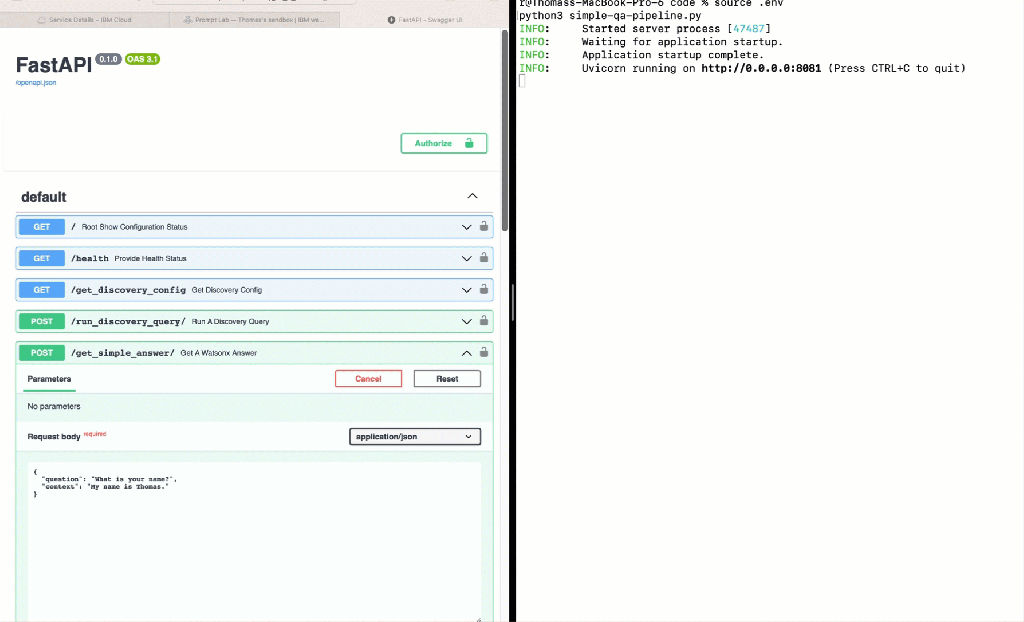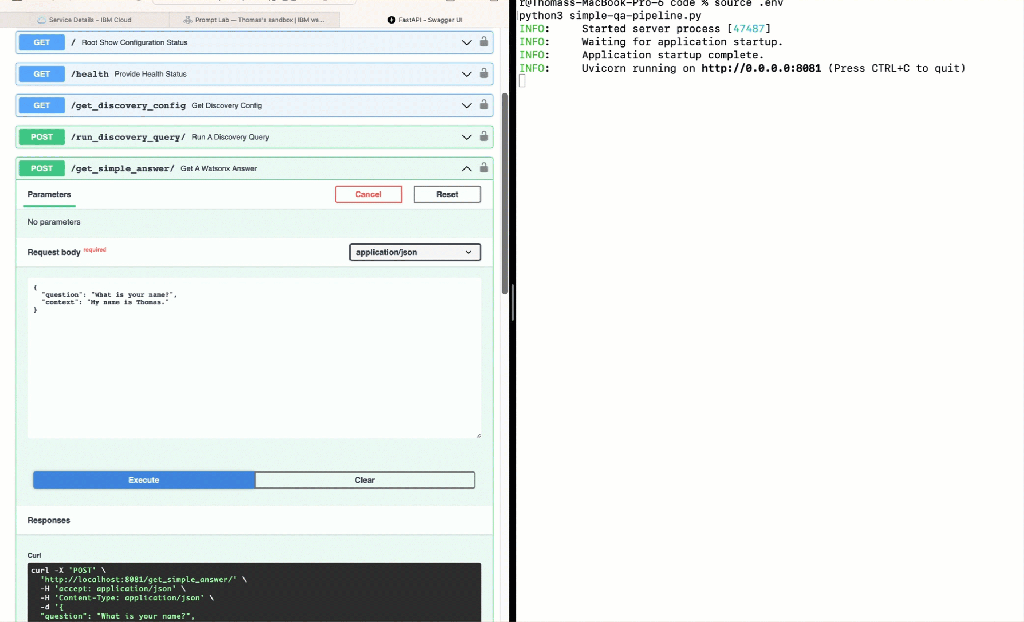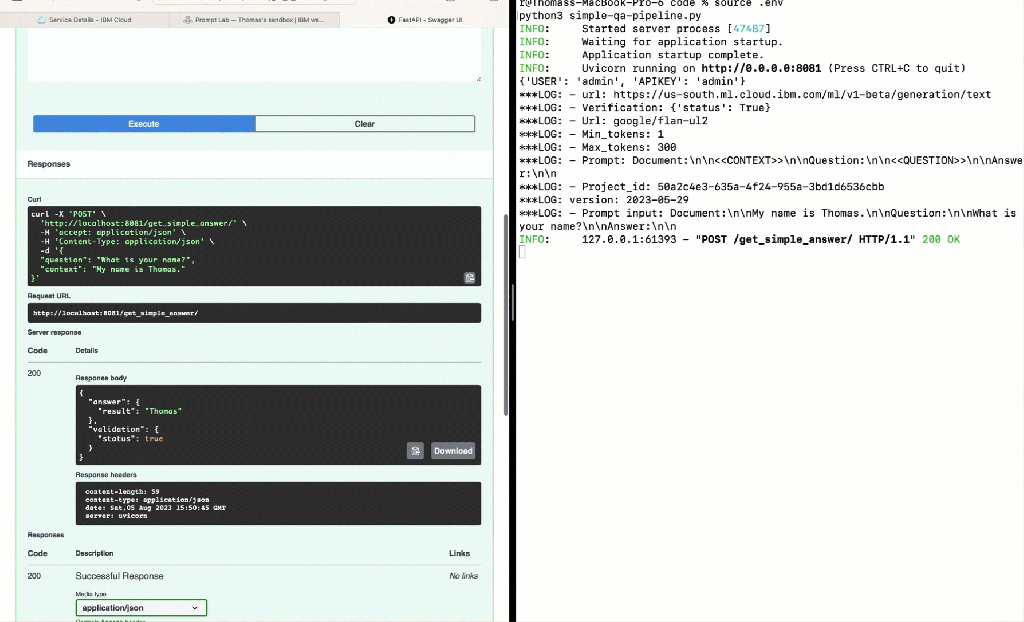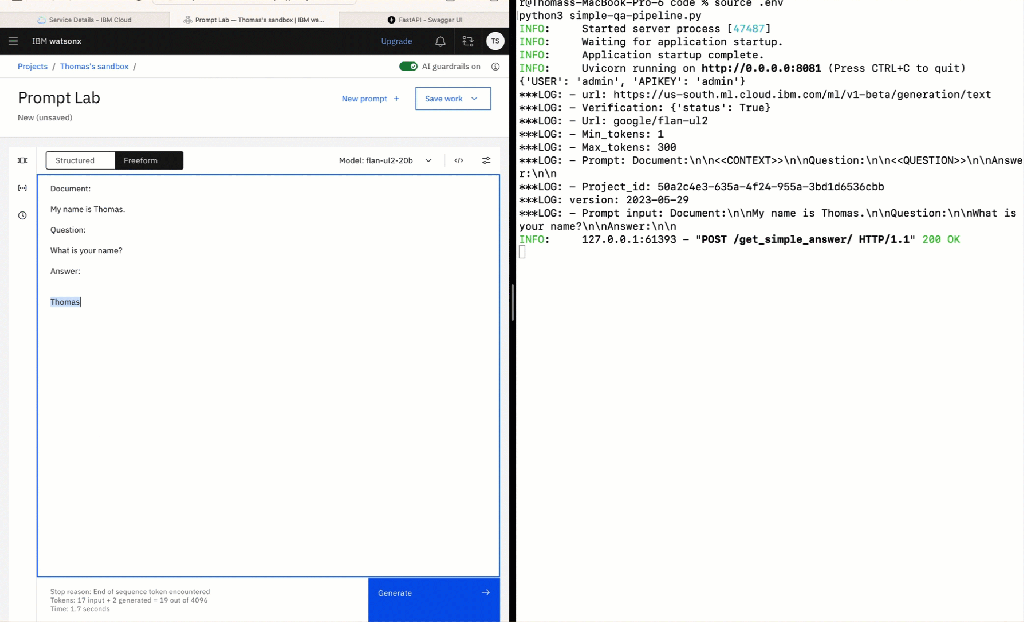
This small test only verifies the watsonx endpoint and not the simple-qa-pipeline with Watson Discovery and watsonx.
In this test, we provide the context and the question for watsonx.
Prompt:
The prompt template was defined before the environment variable WATSONX_PROMPT:
"Document:\n\n<<CONTEXT>>\n\nQuestion:\n\n<<QUESTION>>\n\nAnswer:\n\n"
Test in swagger UI:
First we test the endpoint of our application:
- Insert as question:
"What is your name?" - Insert as context:
"My name is Thomas." - Invoke endpoint
get_simple_answerin the Swagger UI with the given values.
Test in watsonx Prompt Lab:
Second we verify the output in the watsonx Prompt Lab.
- Open
watsonx Prompt Laband insert the following prompt.
Document:
My name is Thomas.
Question:
What is your name?
Answer:
Example:
The following gif shows how the simple test works.
3.4. Source code about: How to access the watsonx REST API
The following code is an extract to the GitHub project. The code shows how to access the watsonx REST API.
def watsonx_simple_prompt(text, question):
watsonx_env, verification = load_watson_x_env()
prompt_context_replace_template="<<CONTEXT>>"
prompt_question_replace_template="<<QUESTION>>"
input_txt=""
documents_txt=text
if (verification):
# 1. Load environment variables
url = watsonx_env["WATSONX_URL"]
print(f"***LOG: - url: {url}")
# 2. Get access token
token, verification = get_token()
apikey = "Bearer " + token["result"]
#print(f"***LOG: - API KEY: {apikey}")
print(f"***LOG: - Verification: {verification}")
if ( verification["status"] == True):
apikey = "Bearer " + token["result"]
model_id = watsonx_env["WATSONX_LLM_NAME"]
print(f"***LOG: - Url: {model_id}")
min_tokens = watsonx_env["WATSONX_MIN_NEW_TOKENS"]
print(f"***LOG: - Min_tokens: {min_tokens}")
max_tokens = watsonx_env["WATSONX_MAX_NEW_TOKENS"]
print(f"***LOG: - Max_tokens: {max_tokens}")
prompt = watsonx_env["WATSONX_PROMPT"]
print(f"***LOG: - Prompt: {prompt}")
project_id = watsonx_env["WATSONX_PROJECT_ID"]
print(f"***LOG: - Project_id: {project_id}")
version = watsonx_env["WATSONX_VERSION"]
print(f"***LOG: version: {version}")
# 3. Build the header with authenication
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Accept": "application/json",
"Authorization": apikey
}
# 4. Build the params
params = {
"version": version
}
# 5. Build the prompt with context documents and question
input_txt = prompt.replace(prompt_context_replace_template,documents_txt)
data_input = input_txt.replace(prompt_question_replace_template,question)
print(f"***LOG: - Prompt input: {data_input}")
# 6. Create payload
json_data = {
"model_id": model_id,
"input": data_input,
"parameters":{
"decoding_method": "greedy",
"min_new_tokens": int(min_tokens),
"max_new_tokens": int(max_tokens),
"beam_width": 1
},
"project_id": project_id
}
# 6. Invoke REST API
response = requests.post(
url,
headers=headers,
params=params,
json=json_data
)
#print(f"Response: {response}")
# 7. Verify result and extract answer from the return vaule
if (response.status_code == 200):
data_all=response.json()
results = data_all["results"]
data = results[0]["generated_text"]
verification = True
else:
verification = False
data=response.json()
else:
verification = False
data="no access token available"
3.5. Setup the related IBM Cloud instance
This example uses IBM Cloud.
3.5.1 Create a Watson Discovery service instance
There is no Lite plan available, but when you create a new IBM Cloud Account, you a free trial period, you can use.
- Create a Watson Discovery instance
- Extract the project ID and collection ID
- If you need additional help, you can visit my blog post Show the collection IDs of IBM Cloud Watson Discovery projects using cURL
3.5.2 Create a watsonx instance
- Visit the watsonx link and get a free trial.
- A
Sandbox projectwill be created for you calledSandbox - The watsonx documentation is available on IBM Cloud
- Open Prompt Lab
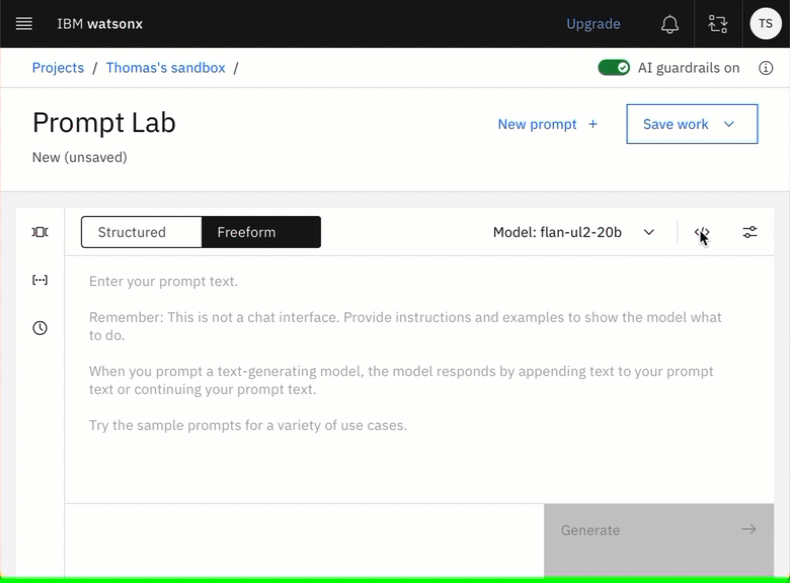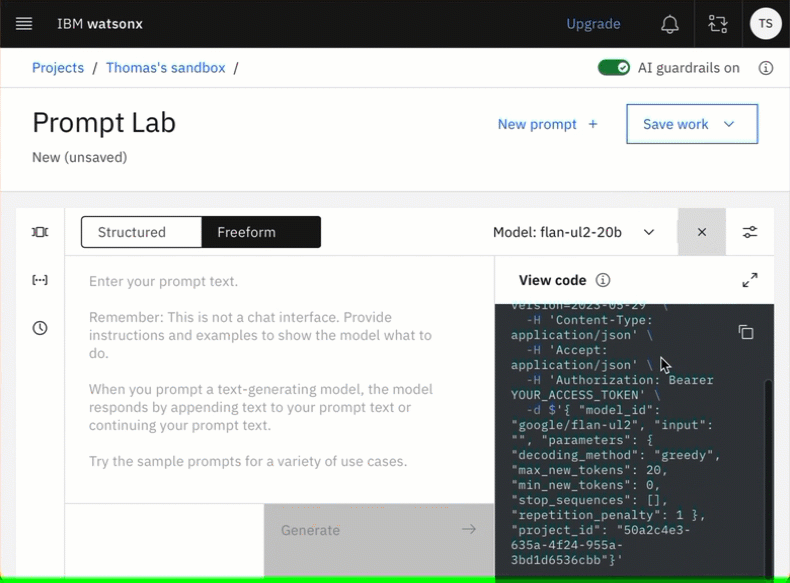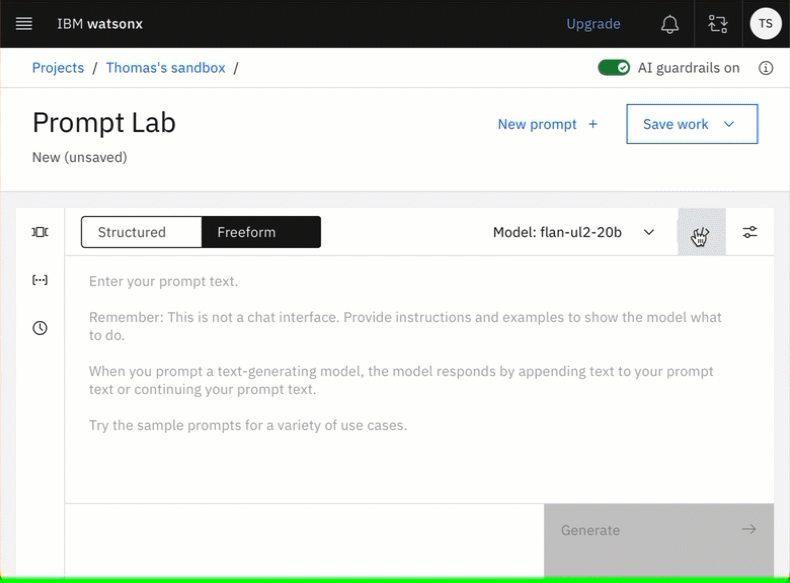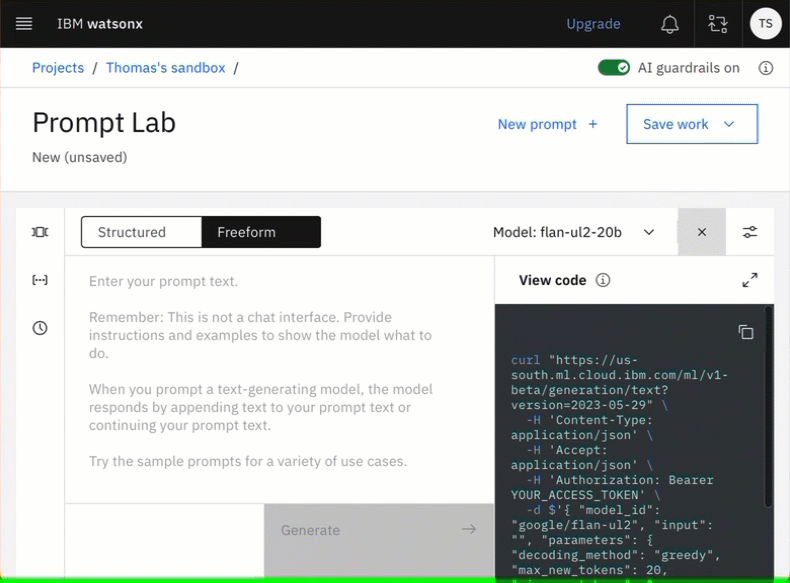
- Open view code
- Create an IBM Cloud API key
Open view code contains your needed curl command, this is very useful.
- With watsonx sandbox project creation following services will be instantiated in your IBM Cloud Account:
The gif below shows how you can access watsonx from your Watson Studion in your IBM Cloud Account.
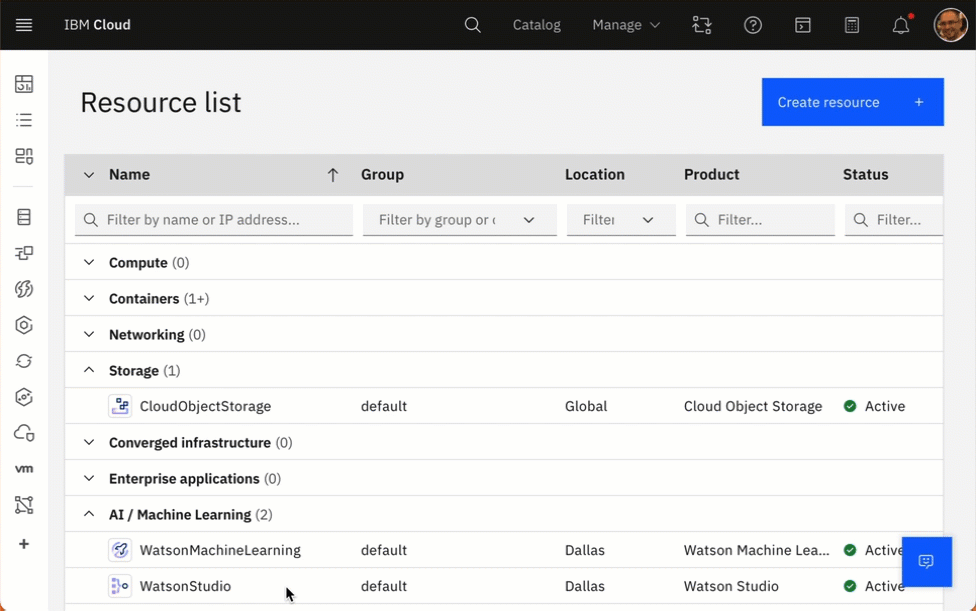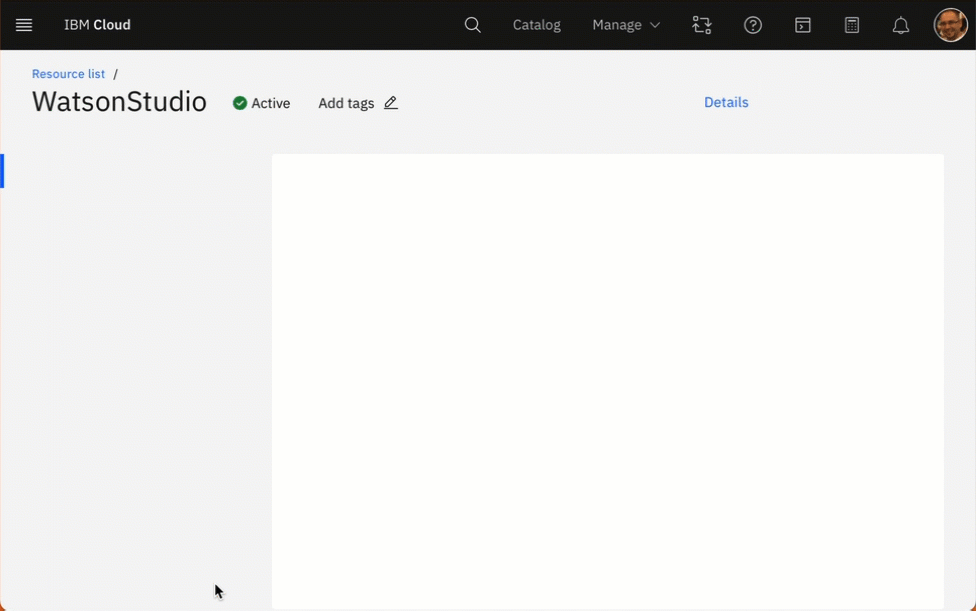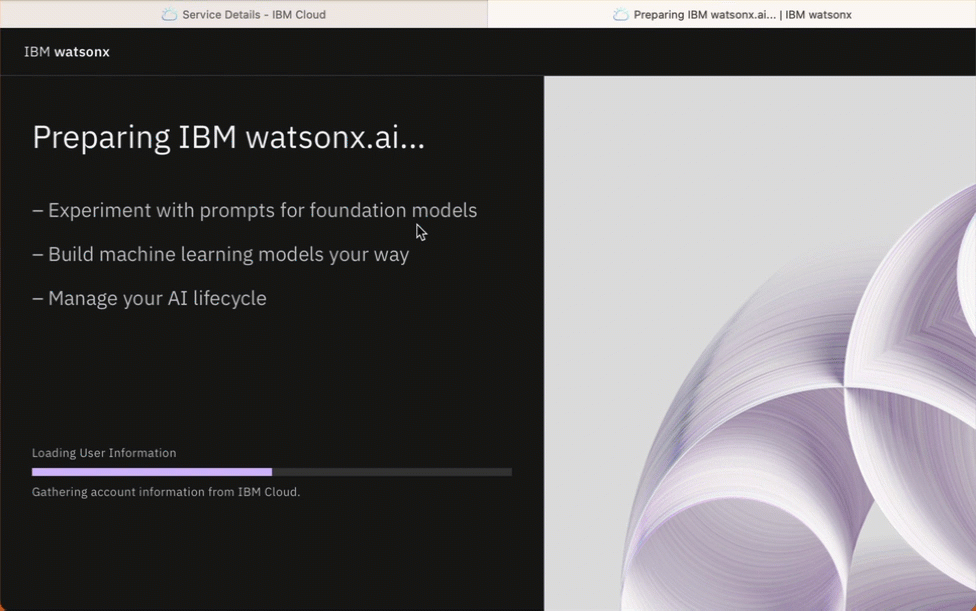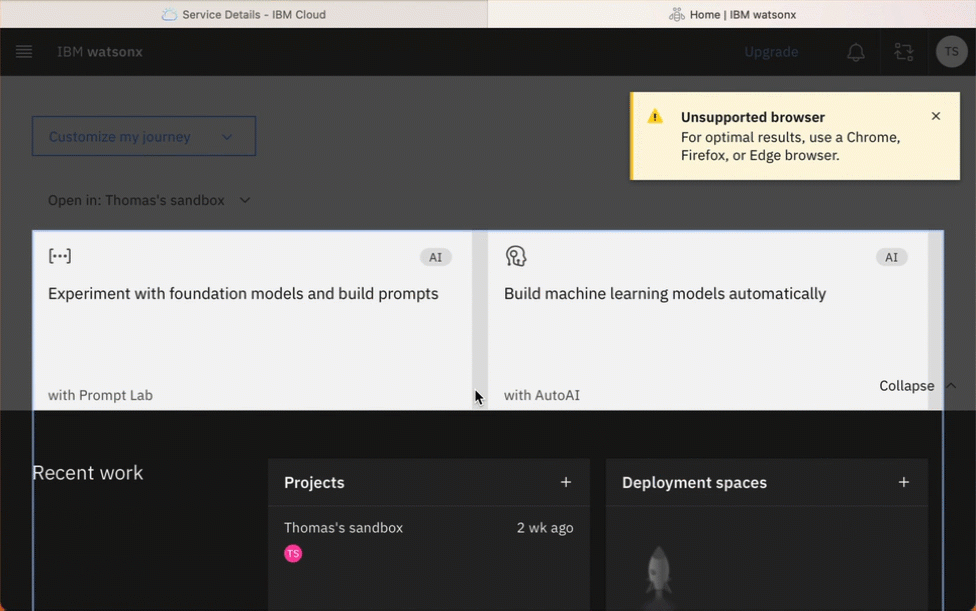
- Simplified dependencies of the created watonx environment in your IBM Cloud Account

4. Useful tools
5. Summary
With fastAPI and Python it was easy and fasted to implement the simple-qa-pipeline. With the automated created Swagger documentation, manually testing the REST API for the simple-qa-pipeline was easy. We can download the OpenAPI spec directly and use its REST API in other integration scenarios like BYOS with in Watson Assistant.
The good REST API documentation from IBM Cloud and watsonx made it easy to use them even without the SDK.
This implementation is close to a realization for a simple example Retrieval-Argumented Generation(RAG) without embeddings and vector database.
I hope this was useful to you, and let’s see what’s next?
Greetings,
Thomas
#python, #fastapi, #watsonx,
#python, #fastapi, #watsonx, #watsonx.ai, #watson-discovery, #swagger, #ibmcloud, #promptlab


This is fantastic. I really like these types of postings with landscape views supplemented by a link-heavy approach. Often, it is all knowledge and indexing one will ever need to get started.
Thank you!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks, and excellent that you recognize these hidden tiny little golden nuggets 😉 … have fun 👍🏻
LikeLike